StatAssist

StatAssist is an integrated tool allowing to explore the properties of various probability distributions. You can access StatAssist in several ways:
- in EasyFit using the menu option
- in Excel using the menu option (EasyFit Professional Edition only)
- directly from the desktop by clicking the icon
Using StatAssist
To select a distribution, use the drop-down list or the menu item. Use the Parameters pane to specify the distribution parameters, and click Apply (or press Enter). As a result, StatAssist will update the associated results.
Graph
The Graph page displays one of the following distribution graphs:
- Probability Density Function
- Cumulative Distribution Function
- Survival Function
- Hazard Function
- Cumulative Hazard Function
The Hazard Function and the Cumulative Hazard Function are available for continuous distributions only. The discrete distributions are generally displayed as vertical lines, but, for some parameter values, they are better displayed as continuous curves since the X axis range gets too large.
Note: The location parameter  of the most
non-negative
continuous distributions is not displayed on the chart legend if it
equals zero. For example, the Exponential distribution with parameters
of the most
non-negative
continuous distributions is not displayed on the chart legend if it
equals zero. For example, the Exponential distribution with parameters
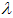 =1 and
=1 and  =0 is
displayed as "Exponential (1)".
=0 is
displayed as "Exponential (1)".
StatAssist calculates the appropriate domain bounds (min. and max. X values) automatically so that the graphs look well for any valid set of distribution parameters. You can also specify the bounds manually.
The graphs can be exported (), copied to the Clipboard (right click on a graph and select ), and printed ().
Calculations
This page displays the following information depending on the selected distribution and parameter values:
- domain type (continuous/discrete);
- minimum value;
- maximum value;
- mode;
- mean;
- variance;
- standard deviation;
- coefficient of variation;
- skewness;
- (excess) kurtosis.
Some discrete distributions may have two modes for some parameter
values. In this case, StatAssist displays the mean mode value. For
example, the Poisson (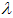 =10) distribution
has two modes (X=9 and X=10), so the value of 9.5 is displayed.
=10) distribution
has two modes (X=9 and X=10), so the value of 9.5 is displayed.
The Calculations page allows to calculate the exact values of the supported functions (PDF, CDF etc.) at a user-defined point x. For continuous distributions, you can also calculate the inverse CDF (also known as the quantile function, or the percent point function), x(P), at some point P. Note that P must be in the range of [0, 1] since it represents probability.
Professional Edition-Specific:
The  icons are intended for copying the corresponding Excel
worksheet functions to the Clipboard. For instance, if you
select the standard Normal distribution and click the
icons are intended for copying the corresponding Excel
worksheet functions to the Clipboard. For instance, if you
select the standard Normal distribution and click the  icon near the Mean field, the following text will be copied:
NormalMean(1; 0).
For more information, please see Using EasyFit with Excel.
icon near the Mean field, the following text will be copied:
NormalMean(1; 0).
For more information, please see Using EasyFit with Excel.
Probabilities
The Delimiters pane allows to specify one or two X values which divide the entire X axis into several intervals (displayed on the PDF graph). For each of the intervals, StatAssist calculates the probability that the variate takes on a value from that interval. This information is displayed on the Probabilities page:
- P (X < X1);
- P (X = X1);
- P (X > X1);
- P (X1 < X < X2);
- P (X < X2);
- P (X = X2);
- P (X > X2).
For continuous distributions, P(X=X1) = P(X=X2) = 0.
www.mathwave.com

